The Life of a Star
As the sun sets, the night sky lights up as stars begin to shine. Stars range in size and color, but have you ever looked at a star and wondered how it formed?
Nebulas
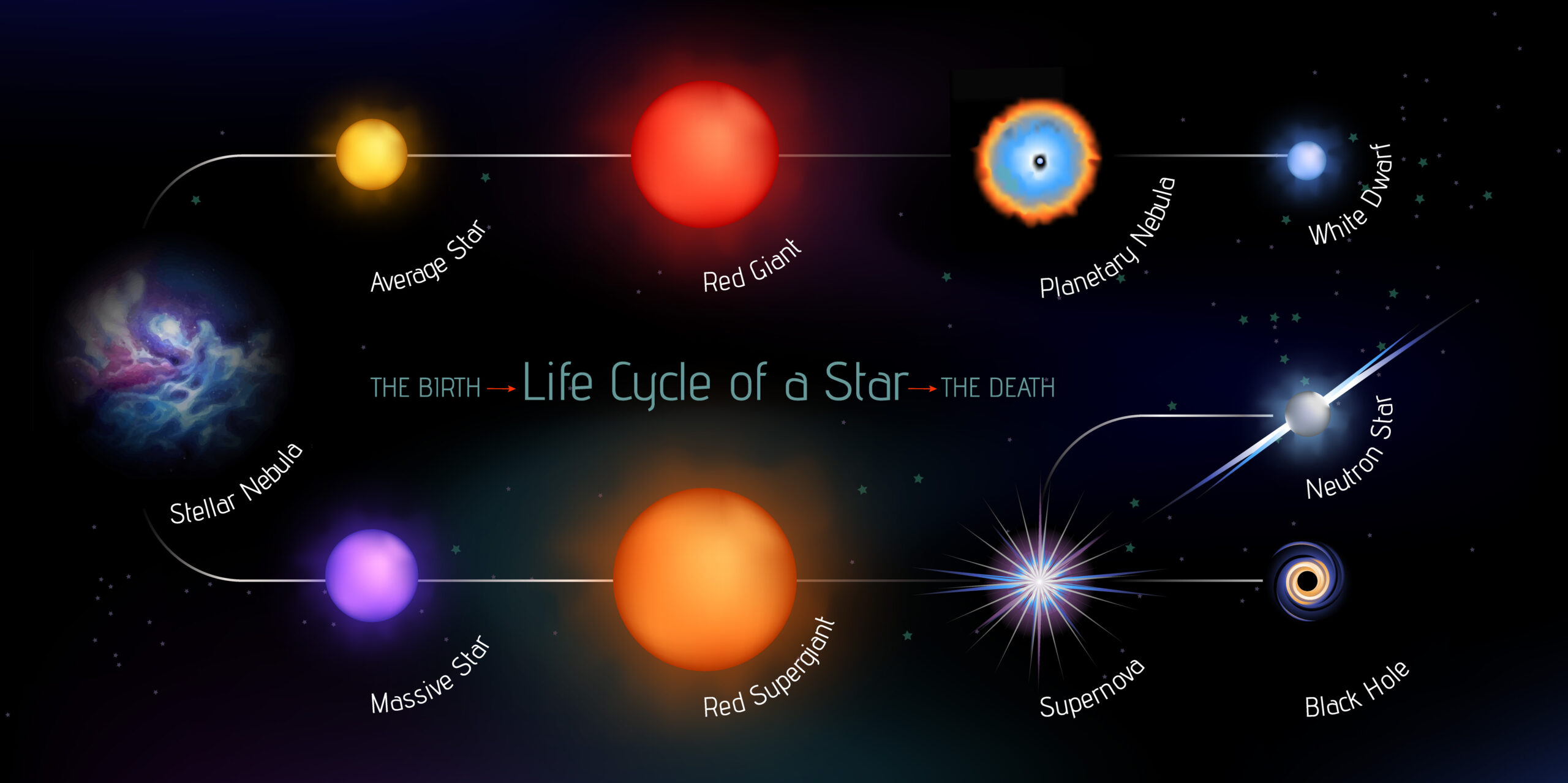
Star formation begins inside nebulas, which are large clouds of gas and dust. With the help of gravity, the clouds collect and begin to collapse. This collapse creates the core that will become a star. The core is called a protostar and while spinning rapidly, heat and pressure rises within. The rising temperature and pressure cause a reaction, which takes us to the next stage of star formation.
The Main Sequence
The main sequence is the second stage of a star’s lifecycle. During this stage gravity and heat within the star has balanced, which stops any shrinking or growing. The star will begin to shine, but what makes the star shine? A reaction takes place within the star’s core, which gives the star the energy to shine and to prevent it from breaking down. The bigger the star, the faster it consumes energy.
After depleting all energy, the star will move onto the next stage of its lifecycle, which is dependent on its size. We will first read about the journey of an average sized star and then we will look at the journey of a massive star.
Average Stars
When an average sized star runs out of energy it enters the phase called a red giant. During this phase, the star gets bigger and changes in color because of the temperature change. After this stage, the star goes through an explosion called a planetary nebula. As time passes, the outer layers from this explosion will fade away. What is left behind are remains known as white dwarfs. The lifecycle of most average sized stars will end as white dwarfs.
Massive Stars
When a massive star runs out of energy it will first become a super red giant. The size and color changes are more extreme because of the magnitude of the star. In time, the super red giant will break down and cause a gigantic explosion known as a supernova. This explosion will lead the star to become either a neutron star or a black hole. We will first read about a regular massive star and then we will learn about a super massive star.
A regular massive star will end as a neutron star. A neutron star is the core of the star that was left from the explosion. A super massive star will end as a black hole. A black hole is a space that holds a lot of strong gravity and consumes other objects.
Each star has their own journey, but they all shine above us at some point in time. Stars are different, but in many ways they are alike. As we continue to explore space, we’ll learn even more interesting facts about star formation. This upcoming summer we will explore the phenomena and beyond with exciting new programs coming to Chabot Space & Science Center!